Laser Spectroscopy News
Nuclear and atomic physicists and nuclear chemists of Mainz University and GSI are closely involved in the EU Innovative Training Network on Laser Ionisation and Spectroscopy of Actinide Elements.
In a proof-of-principle experiment, Nathalie Picqué and Theodor Hänsch from the Max-Planck Institute of Quantum Optics and the Ludwig-Maximilian University have recorded broad spectra with close to 100,000 wavelengths in almost complete darkness.
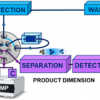
Researchers present concept for a new technique to study superheavy elements combining laser spectroscopy with ion-mobility mass spectrometry.
Marine pollutants are taken up by corals directly from seawater as well as through accumulation in their food shows research from KAUST using cavity ring-down spectroscopy. This is the first time the approach has been used to measure pollutant accumulation.
CERN’s nuclear-physics facility, ISOLDE, has succeeded in performing the first ever laser-spectroscopy measurements of a short-lived radioactive molecule, radium monofluoride.
The interplanar bond strength of graphene has been evaluated by measuring the elastic constant of graphite, demonstrating that the elastic constant of monocrystalline graphite was above 45 GPa, higher than conventionally believed.
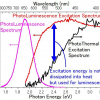
A type of photothermal spectroscopy is being used to measure thermal energy to understand more about the processes of energy-converting systems like leaves during photosynthesis.
Applications are invited for these prestigious awards administered by the Association of British Spectroscopists (ABS) Trust.
Researchers of the University of Basel have developed a new method with which individual isolated molecules can be studied spectroscopically without destroying the molecule or even influencing its quantum state.
A new research project in partnership between academia, companies and the Netherlands Forensic Institute to develop ways to chain analytical techniques together to gain complementary information.
Scientists at the Laboratory for Attosecond Physics have developed a unique laser technology for the analysis of the molecular composition of biological samples.
A prototype of a greatly improved magneto-optic effect measurement device using dual-comb spectroscopy.
Physicists from the University of Bayreuth and the University of Göttingen have discovered a new method for adjusting the extremely short time intervals between laser flashes with exceptional speed and precision.
Attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy has uncovered the interplay between light absorption and electronic screening which could lead to the development of future optoelectronic devices, energy-efficient electronics, magnetic memory devices, spintronics and new types of solar cells.
Together with partners from research and industry, Fraunhofer IAF has developed a hand-held, QCL-based scanner for hazardous substances as part of the CHEQUERS EU project.
For the first time it is possible to measure, simultaneously and with extreme precision, four rare molecular variants of carbon dioxide (CO2) using a novel laser spectrometer.
The ABS Trust is seeking applications for the Gordon F. Kirkbright bursary award and the new Edward Steers bursary, both open to early career scientists.
A review reports on developments and prospects in the field of atomic and molecular broadband spectroscopy with frequency combs.
Researchers in Switzerland and Russia have developed a miniature frequency comb (1 cm3) that can be mass produced.