Conversion of energy is a constant process but measuring the efficiency of this conversion is not an easy task. Quantifying the heat emission of the object that absorbs energy has been proven to be a good indicator. Scientists at the Tokyo University of Science have devised a photothermal spectroscopy technique that can perform this measurement easily and accurately, and this novel technology can shed light on the energy transfer processes in systems ranging from plants to solar cells.
Energy is in a constant universal cycle of use, reform and reuse. Through this process, there are often several situations where energy is received in one form and converted to another form, or even to a non-energy form; photosynthesis is an example for this. However, what is the efficiency of such energy conversion? To put in simple terms, energy conversion efficiency is the ratio of useful output of an energy-converting system like a plant and the total energy that it receives in the first place. This value is important especially in the planning of energy-efficient structures like solar cells. However, although the theory is simple, there is no established method to accurately measure factors that determine light energy conversion efficiency, like total energy or total electrical power generated.
One alternative technique that has been explored for solving this issue is the measurement of heat over light. Everything that absorbs energy tends to dissipate that energy in the form of heat. This release of heat is greater immediately following energy absorption and reduces as time passes. This is in contrast with light emission by systems like “phosphorescent” materials, which absorb energy and only release light much later. Therefore, measuring heat release as a function of excitation light wavelength―the photothermal excitation spectrum (PTES)―can be a viable method to measure energy conversion efficiency. Photothermal deflection spectroscopy is one method for the direct application of PTES. However, very little research has investigated PTES independently of light emission.
The team at the Tokyo University of Science led by Professor Eiji Tokunaga had previously created a Sagnac interferometer photothermal deflection spectroscopy (SIPDS) technique, which improved the efficiency of the existing techniques by one magnitude. Photothermal spectroscopy detects the heat generated when the irradiated light is absorbed by the sample, and therefore, it can measure the absorption spectrum for samples of any shape and with any properties, such as “scatterers” whose transmitted light cannot be measured. Professor Tokunaga says, “Since about 2010, we have been working on increasing the sensitivity of photothermal deflection spectroscopy using an interferometer, and with the collective efforts of everyone including students, we could analyse samples in air that have seldom been analysed before, giving us the ability to measure the absorption spectrum over the entire visible light range. This upgraded technology enabled us to evaluate the quantum efficiency of luminescence or chemical energy conversion.”
Taking this technology a step forward, these scientists, along with Dr Kohsei Takahashi and Dr Naoto Hirosaki from the Sialon Group, National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), have now integrated “balanced detection”, which is essentially a technique to measure small variances in values, into their SIPDS technology. This new innovation uses a white-light lamp as a source of energy and can measure the photothermal excitation spectrum of materials in the air. The scientists noticed that no heat is generated, meaning that light energy is converted to effective energy, so the difference from the absorption spectrum could be measured to determine the light energy conversion efficiency.
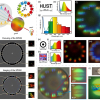
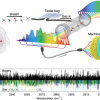
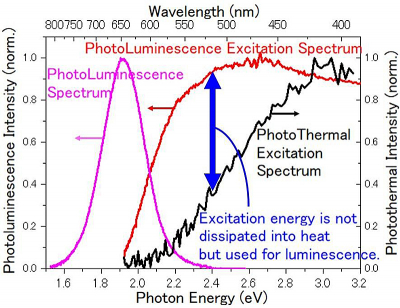
They were able to use this technology to measure the heat spectrum (PTES) of a high-efficiency luminescent red phosphor of white LED, made by NIMS, successfully and compared it with their photoluminescence excitation spectrum (PLES), which showed the amount of light emitted by the phosphor as a function of excitation light wavelength (see figure above). This comparison provided accurate photoluminescence efficiency values of the phosphor as well, which is a measure of how well a substance can emit light. “We can use our technology to measure the thermal relaxation spectra of materials over the whole visible range in the weak excitation limit 50 µW cm–2, which is a never-before-achieved breakthrough”, remarks Professor Tokunaga. Thus, the measurement of energy conversion efficiency, which had previously required expensive and different devices such as phosphors, solar cells and photosynthesis [to measure the converted effective energy (emission energy, electrical energy, chemical energy)], could be done using one simple, unified method. They reported their work in Applied Sciences.
Once developed further, measuring the energy conversion efficiency of even photosynthesis in “live” leaves can be performed. Hopefully, these findings can stimulate and accelerate research aimed at improving the conversion efficiency of substances and realise a society with high energy conversion efficiency.