Surface Analysis News
Hamamatsu Photonics, a global leader in photonics technology, is proud to announce its 70th anniversary, marking seven decades of achievements and contributions to the world of photonics.
Using advanced in situ spectroscopy techniques, scientists at Binghamton University and Brookhaven Lab gain new insights into catalytic oxidation.
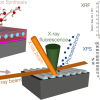
Sequential infiltration synthesis with grazing incidence XRF, XPS and SEM combined with ED X-ray spectroscopy are used for quantification.
Exploiting dark autoionising states for enhancing extreme ultraviolet laser power relevant for advanced ultrafast science applications such as angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy and photoemission electron microscopy.
Hiden Analytical has gained the ISO 14001:2015 environmental accreditation.
Physicists at the University of Texas at Arlington have developed a new technique that can measure the properties of the top-most atomic layer of materials without including information from the underlying layers.
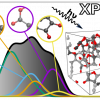
At BESSY II, Auger photoelectron coincidence spectroscopy (APECS) can be used to precisely determine the localisation of d electrons in cobalt compared to nickel and copper.
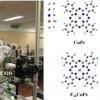
Using ultralow-energy secondary-ion mass spectrometry, researchers are getting a fresh look at MXenes and MAX phases.
A model trained to predict XPS spectra helps researchers to decipher the structure of materials.
The Gordon F. Kirkbright and Edward Steers awards are seeking nominations.
UHV X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy systems have unravelled the Na interaction process at Na/CuPc and Na/F16CuPc interfaces.
Researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University use X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy to discover what gives titanium implants their remarkable biocompatibility, which may lead to more affordable medical and dental procedures.
2022 marks Hiden Analytical’s 40th year of continuous and independent operation in the field of mass spectrometry.
A research team has used x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy to observe charge motions in light-excited molecules of thiouracil, a modified nucleobase.
Raman and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopies and X-ray diffraction have shown the underlying mechanisms leading to failure of energy storage devices.
In a study that used inorganic, physical and analytical chemistry to mimic respiratory droplets that can carry viruses, researchers demonstrated a mechanism that enables multiple mask materials to be protective.
Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, however, have shown that X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy is often used erroneously.
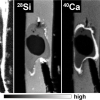
The use of high-resolution secondary ion mass spectrometry imaging indicates that there may be up to 70 times more hydrogen in Earth’s core than in the oceans.
Applications are invited for two awards administered by the ABS Trust.
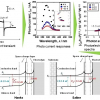
Using time-resolved X-ray photoemission spectroscopy, scientists are for the first time analysing at the femtosecond scale the processes in a model system for organic solar cells.