Spectroscopy News
SIFT-MS has shown promising results for the detection of cancers of the oesophagus and stomach in a large patient trial presented at the European Cancer Congress 2017.
The International Council for Near Infrared Spectroscopy (ICNIRS) are pleased to invite nominations for the 2017 Tomas Hirschfeld Award.
A new interpetation of Raman spectra enables biological carbon to be distinguished from other sources.
X-ray images and XANES reveal battery materials’ chemical reactions in five dimensions: 3D space plus time and energy.
Using ultrafast spectroscopy, researchers from Lund University, Sweden, have successfully measured in detail the flow of solar energy, in and between different parts of a photosynthetic organism. The result is a first step in research that could ultimately contribute to the development of technologies that use solar energy far more efficiently than what is currently possible.
Raman spectroscopy sensor can determine which tissue layer an epidural needle is in and ensure correct delivery of the anaesthetic.
Researchers have nearly doubled the continuous output power of a terahertz quantum cascade laser. Increasing the continuous output power of these lasers is an important step toward increasing the range of practical applications.
Diffuse optical spectroscopic imaging (DOSI) using near infrared radiation can determine fat metabolism and has the potential to help determine if a diet and exercise regime is working.
A new description of electron scattering in the surface layers of samples proposed by the Institute of Physical Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciences in Warsaw significantly speeds up materials analysis and enables a better understanding of what can really be seen in a sample.
Diagnosis of Helicobacter infection is unpleasant for the patient; now an optical absorption spectroscopy instrument can provide diagnosis with 100% accuracy.
Remote simultaneous 3D and spectral imaging will provide direct identification of surface rust and corrosion on structures including bridges and pylons.
Using fNIRS to track the brain activity of both participants, when people are asked to cooperate with a partner, found that males and females had different patterns of shared brain activity.
New broad-band tuneable infrared laser is single-chip, solid-state and offers high-power rapid tuning.
A superconducting insert coil made from a copper-oxide-based ceramic, YBCO, has raised the magnetic field achievable to 25 Tesla.
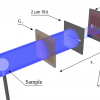
Swiss researchers improve an interferometry technique by utilising the interference fringe, an aspect previously viewed as a nuisance, and increase the efficiency of X-ray flux.
An international research team has shown, using XRF that the iron in Tutankhamun’s dagger blade is of meteoritic origin.
Researchers from Leiden and Delft are using Macro X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry (MA-XRF) to read remains of medieval manuscripts hidden inside the bindings which had been “recycled” after the Middle Ages.
FT-IR spectroscopy can greatly increase the amount of information that can be extracted from a protein microarray. High-quality spectra can be obtained from spots of protein no larger than the diameter of a human hair.
Brillouin spectroscopy has been an effective tool for non-invasively examining materials for several decades, and with a new spectrometer design can now tackle biological samples.
Using time-, energy- and angular-resolved photoelectron imaging a team of researchers has been able to make snapshots of coupled Rydberg orbitals evolving in time during an ultrafast autoionisation process.