Spectroscopy News
A prototype of a greatly improved magneto-optic effect measurement device using dual-comb spectroscopy.
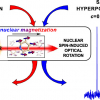
An ultra-fine needle with an integrated chip combines an ultra-sensitive 300-µm nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) coil with a complete NMR transceiver and can be used to probe brain physiology.
Using mass spectrometry, scientists at the University of Southampton have shown how a specific type of symbiotic algae, which lives in coral tissue, is able to adapt and survive the hotter seawater temperatures caused by global warming.
Physicists from the University of Bayreuth and the University of Göttingen have discovered a new method for adjusting the extremely short time intervals between laser flashes with exceptional speed and precision.
Researchers at ETH Zurich have developed a chip-based, infrared spectrometer based on waveguides rather than an interferometer.
Researchers from University of Tsukuba develop a new method that reveals the unique fluorescence signatures of individual cells in mixtures of bacteria, fungi and yeast.
Using ultrashort pulsed laser technology, infrared and Raman spectroscopy can be performed simultaneously.
NIR spectroscopy has been used to detect the presence of cholesterol in the arteries of mummified people who lived thousands of years ago.
Charge transfer and intermolecular interactions in artificial photosynthesis that occur on a ps scale have been directly observed.
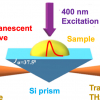
fNIRS could help diagnose pain in non-communicative patients.
Markes International has received two Queen’s Awards for Enterprise in the “Innovation” and “International Trade” categories.
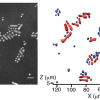
Researchers from the Faculty of Science at the University of Oulu have increased the sensitivity of the NMO spectroscopic method with promising applications for materials studies.
MOBILion’s ion mobility separations technology—Structures for Lossless Ion Manipulation (SLIM)—is to be integrated with Agilent’s Q-TOF mass spectrometry platform.
Scientists at Münster University use dual-beam lasers to increase the resolution of MALDI MS imaging.
Scientists have designed an ultra-miniaturised device that could perform spectral imaging on single cells without the need for a microscope or perform spectroscopic analysis from a smartphone.
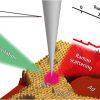
Tip-enhanced “resonance” Raman scattering can be used to investigate a specific chemical structure at nanoscale and even at the single-molecule level, and also provides a new approach for the atomic-scale optical characterisation of local electronic states.
Shimadzu has opened a branch office in Sweden, which will market Shimadzu’s full range of analytical instrumentation solutions.
At the EUROISMAR 2019 meeting, Bruker and its scientific collaborators are presenting 1.2 GHz high-resolution NMR data that has been acquired using a new 1.2 GHz 3 mm triple-inverse TCI CryoProbe.
XRF mapping, infrared and hyperspectral imaging reveal early designs for Leonardo da Vinci’s The Virgin of the Rocks.
Specac opens new headquarters including manufacturing, office and demonstration facilities.