Magnetic Resonance News
Sir Martin Wood, founder of Oxford Instruments died on 23 November at the age of 94 after a short illness.
A deeper understanding of how unwanted elements within bio-manufactured proteins bind to the molecules developed to remove them could help researchers make purity processes more efficient.
The agreement allows numares to exploit preliminary work of Oxford University on Multiple Sclerosis biomarkers for the development of an IVD test able to detect disease progression earlier.
Hungarian and German researchers have jointly developed a NMR method that reveals changes in the structure of proteins more efficiently and accurately than before.
The New York/New Jersey Section of the Society for Applied Spectroscopy are seeking nominations for their 2022 Gold Medal Award.
NMR spectroscopy and other analytical techniques were used in the study of the binding of EGCG, a green tea compound that may increase levels of p53, a natural anti-cancer protein.
A deep neural network has been developed to analyse NMR data faster and with the same accuracy as human experts.
New research at Griffith University has streamlined the process of identifying the structure and molecular weight of compounds by using a single NMR method.
The Körber European Science Prize 2021, worth one million euros, is to be awarded to University of Cambridge chemist Professor Clare Grey, one of the UK’s leading battery researchers.
For the development of drugs or vaccines against COVID-19, research needs virus proteins of high purity and the ability to determine their three-dimensional protein structures.
A method, based on nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, allows for simulation and visualisation of magnetic-field-induced electron currents inside gold nanoparticles.
numares AG has made a 510(k) submission to the US Food and Drug Administration for its AXINON® IVD System, a NMR-platform for AI-driven, metabolomics-based diagnostics.
Applications are invited for two awards administered by the ABS Trust.
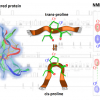
Scientists have succeeded for the first time in the direct spectroscopic detection of the binding of the “Parkinson protein” α-synuclein to lipid membranes in the cell.
Oxford Instruments, Oxford University and Henry Royce Institute have agreed an R&D collaboration to use benchtop NMR to develop new methods to monitor reactions in battery cells.
An NMR-based serum test has been shown to assess kidney function and provides for a more precise estimation of glomerular filtration rate.
Professor John Mallard played a crucial role in the development of two of the world’s most important medical technologies: magnetic resonance imaging and nuclear medicine imaging.
Researchers from the Sheffield Institute for Translational Neuroscience (SITraN) have used 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy to measure the function of mitochondria in patients with motor neuron disease.
University of Tsukuba researchers have used electron spin resonance spectroscopy to take a molecular-level look at what happens in perovskite solar cells when they are operating, to determine the factors that affect their performance.
A new 1 GHz solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrometer is now at field at University of Warwick.